Threat Explainer: Provide Chain Attacks
Let’s point out that you’re confident inside your security position. You have endpoint security set up, firewalls defending the perimeter, and phishing filter systems on incoming e-mail. You’ve leveraged equipment to check on for anomalies in your system visitors, rolled out an SSO remedy, and implemented procedures to securely remotely hook up to the network.
It is created by these defenses harder for poor actors to compromise your company. Strong security position is more prone to push all poor actors to move to other, less protected targets.
It’s as of this crossroad, between inspiration and less secure targets, where offer chain attacks sit. Poor actors can look for disadvantages to attack always. It might be your weakest point isn’t inside your own organization, but within among your suppliers. You have faith in their products, counting on them to carry out business. Sadly, if their security position isn’t as mature as yours, attackers can exploit that faith and utilize it in attacks.
This is exactly what a supply chain attack is. In these attacks, poor actors compromise a second organization that supplies providers or software program to a primary, target organization. Their goal would be to compromise the principal target when they utilize the service or software of the secondary target. In a nutshell, they piggyback on the secondary focus on to obtain their malicious code in to the primary target.
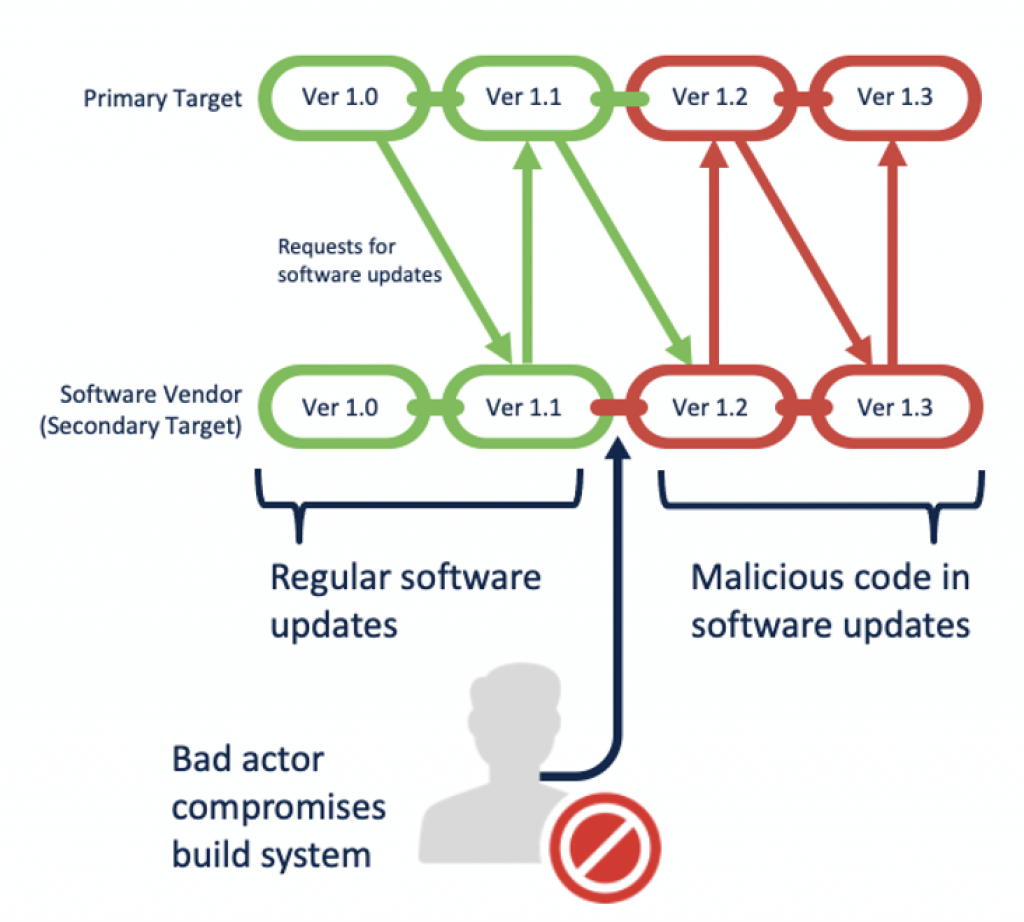
The way the attack functions
There exists a general design in supply chain attacks. First, the poor actors gather what info they are able to find concerning the primary target. The attackers measure the suppliers of those products and then select a secondary target. This secondary target becomes the fulcrum of the attack now.
Next, the poor actors try to compromise the secondary focus on. The true ways each goes about doing so will change, choosing the road of least resistance frequently. They could try out anything from spear phishing to exploiting vulnerabilities at the system edge. The decision shall largely depend where in fact the attackers perform reconnaissance to find out a successful breach.
Once inside, the attackers laterally move, their objective getting to compromise the secondary focus on’s software build program often, where in fact the source code because of their software program is stored, updated, and compiled. Among the easiest methods to accomplish that is usually by compromising a developer’s device, or their credentials, attaining the mandatory access. With usage of the build system, the attackers can place malicious code surreptitiously, such as a RAT or backdoor, into the software program involved. The secondary target, unacquainted with the current presence of malicious program code, compiles the most recent updates, indications the binary, and releases it then.
At this true stage the attackers await the primary business to download and install the compromised update. The malware attackers have admission in to the primary organization they designed to compromise now.

Notable illustrations
There are many supply chain attacks which have made headlines. Year probably the most notable happened last, when poor actors compromised software improvements to SolarWind’s Orion IT administration software program . The attackers were able to stay concealed for months, where several US federal government agencies and corporations had been compromised .
But this attack was definately not the first to work with a source chain as a vector. In 2017, the wiper malware NotPetya is thought to have started its pass on by leveraging the update program of the Ukrainian taxes software program, M.E.Doc . This strike resulted in widespread compromises in the Ukraine, and around the world , resulting in vast amounts of dollars in damage.
Year later that same, bad actors were able to put in a backdoor in to the popular PC upkeep device, CCleaner . The compromised variations had been downloaded over 2.27 million times , though just a few these installs were geared to get a secondary payload.
Supply chain attacks possess existed for a genuine number of years. While relatively infrequent, likely because of the high growth and sophistication complexity, their potency make sure they are a viable substitute for well-funded and motivated attackers.
The protection problem
The toughest part about supply chain attacks is that the vector used to compromise the principal target is hidden within legitimate software. This makes offer chain attacks difficult to safeguard against incredibly, presenting a true amount of challenges.
First, source chain attacks compromise software program that your organization makes use of and trusts already. Inserting bad program code into trusted software helps it be difficult to recognize the malicious action notoriously.
Great security and software engineering practices within suppliers certainly are a solution to combat supply chain attacks indeed. However, audits of providers require no small expense of time and money, and don’t always scale over the true number and selection of suppliers used by confirmed company.
Patching is really a vital section of any security technique. It is especially ironic that regarding so many offer chain attacks, the malicious functionality is written by abuse of the update and patching mechanism by awful actors.
This presents a catch-22, whereby an errant patch you could end up a supply chain compromise, however, not patching may lead to other security risks, such as for example exploitation via unpatched vulnerabilities.
Captured in the work
Provided the enormity of the duty of detecting a provide chain attack before awful actors gain access, generally, another approach will be needed. The silver lining will be that, while gaining access could be appeared at as the hallmark of an effective supply chain assault, it’s still just the beginning with regards to bad actors’ ultimate targets.
The actual fact remains that the machine by which attackers gain their initial access isn’t usually their ultimate location. An attacker will need to traverse a system still, moving to access their goal laterally. Also, if stealing details is their aim, they’ll have to exfiltrate said information still. And through everything, they will have to perform order and control exercise to teach the malicious software program to do what they want it to do.
These are all excellent touchpoints to detect, block, and remediate this attack. Having policies set up to detect such action can go quite a distance to alerting to a source chain attack.
For instance, look out for any of the next:
-
- Search for unauthorized adjustments or unusual software program additions on endpoints. Attackers modify endpoints often, or install software program like webshells, to help expand their attacks.
-
- Keep track of for unexpected usage of credentials. Compromised devices enable threats to log into various other devices on the system.
-
- Pay particular focus on key techniques, such as energetic directory servers or some other domain controllers.
Concentrating on reaction
With avoidance being difficult, or even an unattainable goal, reaction becomes a far more viable method to defend against offer chain attacks. One method to do this has been extended recognition and response (XDR) options . Such options give visibility across systems, endpoints, and programs to investigate, hunt, and remediate episodes.
The threat response feature in Cisco SecureX is ideally suitable for help out with cases like supply chain attacks. Being an integrated safety architecture that automates integrations across Cisco Safety products, it simplifies risk investigations and responses greatly. And these reaction and investigation abilities combined into one easy, efficient workbench.
If you suspect a source chain attack, it is possible to drill down to notice where specific exercise began. It is possible to track it over the network to find the larger picture then. Afterwards, it is possible to take corrective action straight from the interface after that, blocking suspicious items at that moment.
A critical element of this presence is Cisco Secure Endpoint , providing both threat reaction and hunting capabilities within a solution, leveraging the billed power of cloud-centered analytics. Powerful tools like document trajectory and gadget trajectory use Protected Endpoint’s continuous analysis features to show you the entire scope of a threat and identifies all impacted apps, processes, and systems.
Network visibility is crucial in detecting attacks because they attempt to shift throughout the network. Equipment like Cisco Secure System Analytics can detect suspicious and unforeseen activity on the system, along with data exfiltration, plan violations, along with other sophisticated techniques utilized by attackers. Safe Network Analytics may analyze encrypted visitors for unusual activity still.
Furthermore, use Secure Network Analytics with Identity Services Motor (ISE) to segment the network. Segmentation shall not stop the supply chain attack. Malicious activity can make more chances for recognition. With ISE, understand who, what, where, and how endpoints and gadgets are connecting. ISE permits software-defined accessibility and automates system segmentation even.
Detecting anomalies in program behavior might help identify a provide chain attack. To get this done, options like Cisco Secure Workload can offer the opportunity to baseline the standard behavior of one’s applications, enabling you to identify anomalies or even suspicious behavior quickly.
This can all be considered a little overwhelming. If you’re searching for assistance in working with a offer chain strike, Cisco Talos Incident Reaction (CTIR) is here now to greatly help. Whether you’re searching for a crisis incident response, assist with playbooks, readiness assessments, threat hunting, purple group exercises, or even more, CTIR can provide.
<br>

You must be logged in to post a comment.