Dynamic Service Chaining within a Data Middle with Nexus Infrastructure
Within an application-centric data center, the network will need maximum agility to control workloads and incorporate companies such as for example firewalls, load balancers, optimizers and proxies. These network solutions enhance compliance, security, and optimization in virtualized information cloud and centers systems. Data center ops groups need an elegant solution to insert support nodes and have the capability to automatically redirect visitors using predefined guidelines as operations change.
Enterprises running their information centers around the Nexus 9000 and NX-OS platform is now able to seamlessly integrate services nodes to their data middle and edge deployments utilizing the new Cisco Enhanced Plan Based Redirect (ePBR) to easily define and manage guidelines that control how visitors is redirected to person services.
Challenges with Service Services and Insertion Chaining
The biggest challenge with regards to introducing service nodes in a information center is onboarding them in to the fabric, and creating the traffic redirection guidelines subsequently. Today, you can find two ways of applying traffic redirection guidelines – by influencing the visitors path making use of routing metrics, or by selective visitors redirection using policy-structured routing.
The task with using routing to influence the forwarding path is that traffic traverses exactly the same path. This eventually ends up making the service node a bottle neck often. The only practical solution to achieve scale is definitely by scaling the node vertically, that is limited and expensive by the extent the node could be expanded.
Plan Based Routing (PBR) guidelines are also complex to keep up since separate guidelines are needed for ahead and reverse traffic instructions to be able to maintain symmetry for stateful assistance nodes. In addition, whenever there are multiple program nodes in a chain, maintaining PBR tips to redirect traffic throughout them increases complexity a lot more even.
Introducing Enhanced Plan Based Redirect
NX-OS version 9.3(5) provides Enhanced Plan Based Redirect. The purpose of ePBR would be to solve a few of the problems with existing redirection guidelines. The bottom line is, ePBR:
- Simplifies onboarding provider nodes in to the network
- Creates selective visitors redirection rules across an individual node or perhaps a chain of support nodes
- Auto-generates reverse redirection guidelines to keep symmetry across a continuing service node chain
- Provides the opportunity to redirect and load-stability
- Works with pre-defined and customizable probes to keep track of the fitness of service nodes
- Supports the opportunity to either drop visitors, bypass a node, or even fallback to routing lookup whenever a node in the chain fails
ePBR supports most of these abilities across a fabric jogging VXLAN with BGP EVPN, in addition to a classic primary, aggregation, access data middle deployment, at line price switching, without penalty to throughput or even performance. Let’s appear at three ePBR make use of cases.
Use Case 1: ePBR for Selective Visitors Redirection
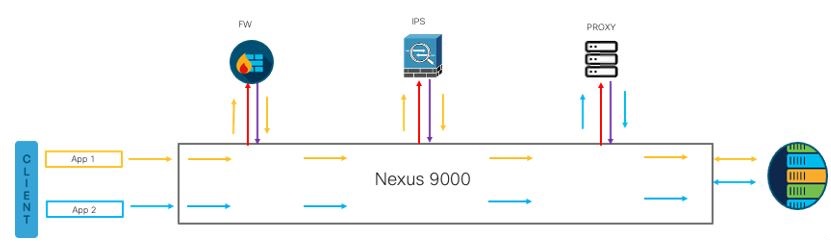
Various applications may need redirection across different models of service nodes. With ePBR, redirection guidelines can match application visitors using Source Location IP and L4 ports and redirect them across various service nodes or services chains. In the diagram below, client visitors for App 1 traverses the IPS and firewall, whereas Software 2 traverses the proxy before achieving the server. This versatility that ePBR enables clients to on-board multiple apps on the network and adhere to security requirements.

Use Case 2: Selective Visitors Redirection Across Dynamic/Standby Assistance Node Chain
In this use case, traffic from clients is redirected to a load-balancer and firewall services chain, before being delivered to the server. Making use of probes, ePBR intelligently tracks which node in each cluster can be energetic and immediately redirects the visitors to a new energetic node if the initial energetic node fails. In this illustration, the ongoing service chain is inserted in a fabric operating VXLAN. As a result, traffic from customers is redirected to the dynamic firewall and the dynamic load-balancer always.

Use Case 3: Load-Balancing Across Provider Nodes
With exponential growth in traffic, ePBR can load-balance across service nodes in a cluster intelligently, providing the opportunity to scale the network. ePBR ensures symmetry will be maintained for confirmed flow by ensuring traffic in both forwards and reverse instructions is redirected to exactly the same assistance node in the cluster. The example below exhibits how traffic in the mobile packet primary is load-well balanced across a cluster of TCP optimizers.

Improving Operational Performance with Innovations within Cisco ASICs and NX-OS
Cisco continues to supply value to your customers by completely leveraging features designed into Cisco ASICs and improvements in NX-OS software program. ePBR enables the fast on-boarding of a number of services into information center systems, and simplifies how visitors chaining rules are set up, reducing period spent provisioning providers and improving general operational efficiency thus. For more information about ePBR make reference to the Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS ePBR Configuration Guide.

You must be logged in to post a comment.